Asarum, Asarabacca, Xi Xin 细辛
Asarabacca, Wild Spikenard, Hazelwort
Asaroon (Unani)
Xi Xin (TCM)
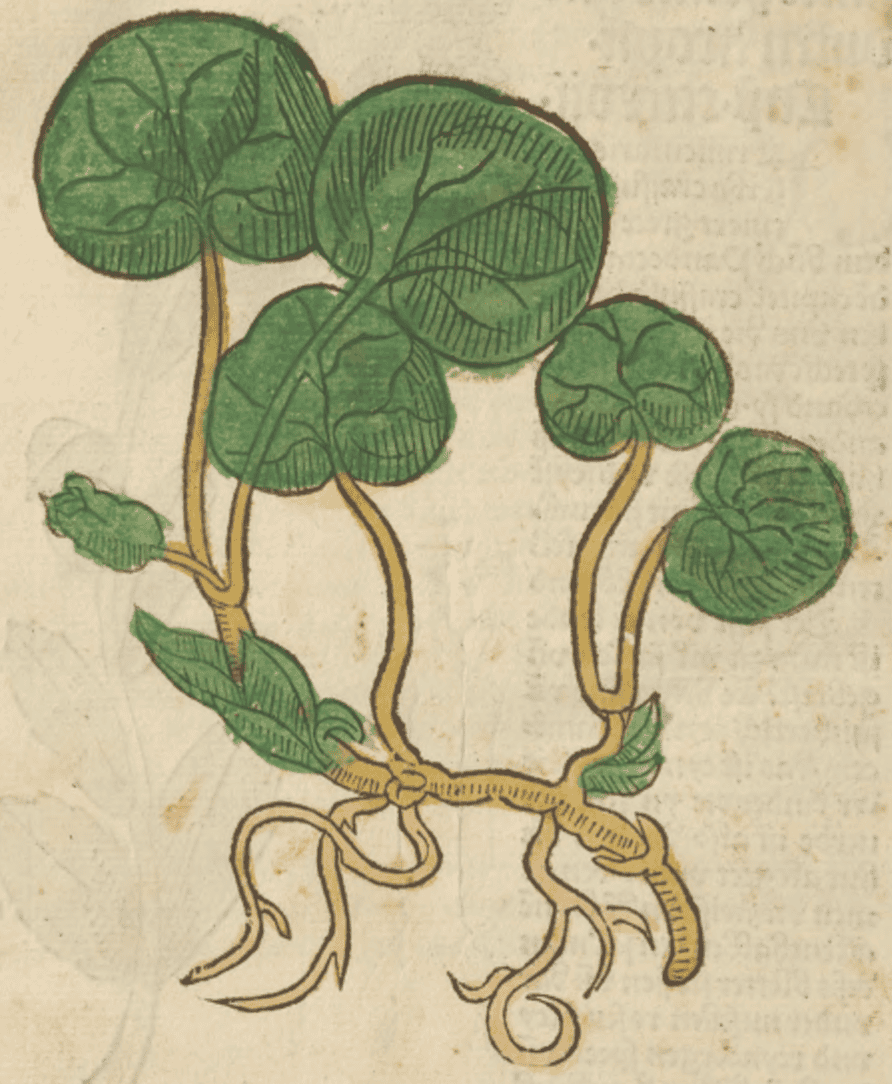




Gart der Gesundheit, Cuba, 1485
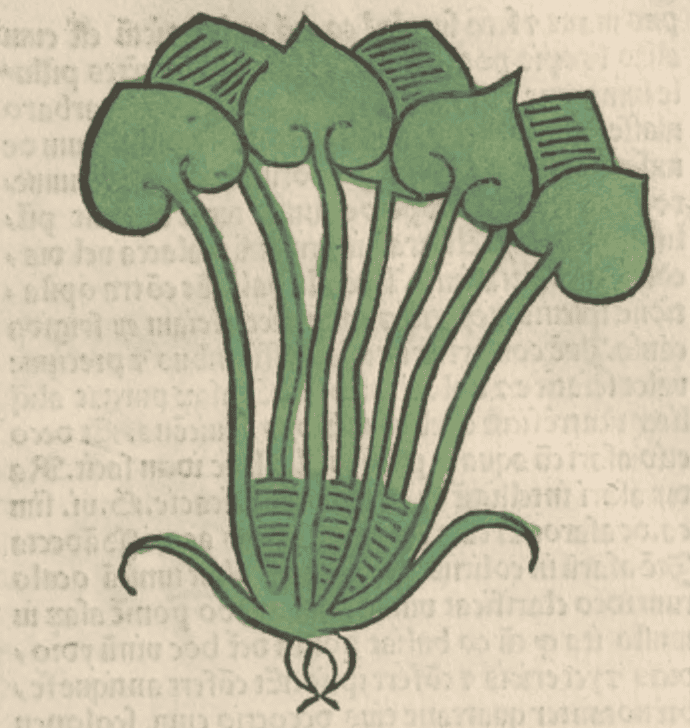

Herbarius latinus, Petri, 1485

Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563

Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
Asarum europeum,
Flora von Deutschland (21), Kohler, 1885

Chinese Asarum Xi Xin (A. sieboldi)
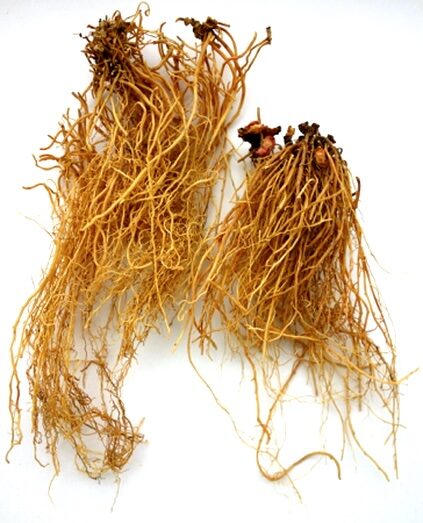

Asarum Xi Xin root (Adam, 2019)
Botanical name:
Asarum spp..
1. A. europeum (syn. A. officinale, A. rotundifolium) is the standard Western species
2. A. heterotropoides, A. sieboldi, A. chinense (syn. A. fargesi), A. crispulatum, A. ichangense, A. delavayi, etc. (TCM)
Over 30 different species are used in China.
The Western and Eastern varieties are very similar in appearance, quality, function, and use.
Parts used:
Root; less commonly the leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Hot, dry. Pungent. Slightly Toxic
Classification:
2A APERIENT MEDICINES. 2Q. ANODYNE.
3E. DIURETIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE. 3J. INCREASE SEMEN. 3Q. ANTHELMINTIC
4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4k. ARTHRITIC
TCM:
A. Clears Exterior Wind-Cold
M. Warm to Expel Cold
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Cold, Promotes Sweat, Resists Poison (TCM, West):
-Wind-Cold type Cold, Flu
-Sinusitis, acute nasal congestion
-acute pain associated with Wind-Cold; Headache, Toothache, muscular aches and pains
-Chronic and Tedious Fevers; Tertian and Quartan Fevers
-half–1 dram (with wine) given before the Fit in Fevers can cure in 3 doses;
-It relieves the shivering and causes the hot fit to be more gentle (Pemell, 1652)
-‘Warms the whole body’. (Galen)
2. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough (TCM, West):
-Cough, chronic Bronchitis, Asthma; also Pneumonia
-Cough with profuse, watery sputum (Cold Phlegm) in TCM.
3. Clears Cold, Wind and Damp, Moves the Blood, Eases Pain (TCM, West):
-Arthritis, Rheumatism, Sciatica
-Chest Pain, Angina Pectoris; Abdominal Pain
-Headaches and Migraine from Blood stagnation or Wind-Cold obstruction
-useful for pain or obstruction anywhere in the body from Blood obstruction as a result of Cold, Damp, Phlegm or Bruising
-“suitable for thos suffering from … chronic hip disease”. (Dioscorides)
-“Asarum drives away all internal pains of the body, and warms the internal members, which are chilled, if one drinks it”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-“Its decoction is used in all kinds of opilations of the liver, spleen, and all the organs”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-dissolves Wens (sebaceous Cysts) and hard Swellings; ‘eminent against the Kings Evil [Scrofula]’. (Salmon)
–Culpeper said the root “may prove beneficial in such as have Cancers, or old putrified Ulcers, or Fistulas upon their bodies”.
4. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation (TCM, West):
-strongly promotes Menstruation; Amenorrhea; Chlorosis, Dysmenorrhea
-useful for gynecological disorders associated with stagnation; Cysts, Fibroids, Endometriosis etc.
-“They also draw down the menses”. (Dioscorides)
-“Asarum water or a decoction of it is drunk, expelling both living and dead foetuses, which is why it is not to be given to pregnant women”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
5. Clears Cold and Damp, Promotes Urine (West):
-Edema, Dysuria; urinary obstructions
-“suitable for those suffering from edema”. (Dioscorides)
-“Asarum stimulates urine, strengthens the bladder and the loins”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
6. Clears Phlegm, Promotes Vomiting:
-whole plant in powder, or 2 drams infused in a pint of white wine (West)
-fresh leaves are strongest to promote vomiting
7. Externally:
-the powdered leaf has traditionally been used as a sneezing powder in chronic Rhinitis and Sinusitis.
-“
If one anoints the spine with Asarum oil, it provokes a fever and opens obstructions”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-“If the head is washed with a decoction made from Asarum, it strengthens the brain”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-as a snuff for Nasal Polyps (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
-decoction is used as a wash for swollen gums (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Dose:
1. With Hydromel as a Purgative
2. With wine to move the Blood and open Obstructions.
Infusion or Brief Decoction; 1.5–6 grams
Powder: 500mg–3 grams; The powder was commonly given in doses of half–1 dram (2–3.8 grams) in the west.
The powder in doses of 1–2 grains is stimulant; ½–1 scruple is emetic. (Sobernheim, 1840)
It was said if very finely powdered, it promotes Vomit and Urine; if coarser powder is used, it purges by stool. (West)
For Malarial and Chronic Fever, 3–4 oz. doses of the distilled water was taken every morning.
Comment:
Asarum is an important medicine in both East and West. The Chinese variety and uses are compatible with the Western variety and its uses, and the Chinese variety was known and used in the West synonymously (see History below). Its actions derive from its hot, piercing and pungent qualities which penetrate through obstructions, open the capillaries and skin pores to resolve obstructions of Wind, Cold, Damp, Phlegm and Blood.
It is very useful for acute Wind-Cold Cold and Flu with nasal congestion, feeling of cold, cough with watery sputum and headache. It is also an important ingredient in formulas to clear Cold and Damp from the muscles and joints. In the West it was an important ingredient in a number of formulas used for ‘Obstruction’, usually a mixture of Phlegm, Damp with Qi and Blood Stagnation.
Substitutes:
1. Calamus is an acceptable substitute.
2. Avicenna recommended Ginger
3. Zedoary (Unani)
4. Polypody with half part Acorus and sixth part Amomum (Mesue)
5. When used for Joint pain or Blood stasis, Corydalis Yan Hu Suo is often substituted.
6. Herb True Love.
7. As an emetic: Ipecac, Violet root
8. Asarum was often used for Snake Root
Main Combinations:
1. Cold, Flu, Asarum with Angelica and fresh Ginger
2. Nasal congestion, Asarum with Peppermint and Angelica Bai Zhi. (TCM)
3. Quartan Fever, Asarum, Scolopendra, Senna leaf (Botanicon Continens Herbarum, Theodore Dorsten, 1540)
4. Cough, Wheezing, Asthma:
i. from Wind-Cold and Phlegm, Asarum with Ephedra. (TCM)
ii. from Cold-Phlegm, Asarum with Schisandra Wu Wei Zi. (TCM)
iii. Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema from Cold-Phlegm and fluid obstructing the Lungs, Asarum with Ginger (Gan Jiang), Poria Fu Ling, Honey-fried Licorice (Zhi Gan Cao), Schisandra Wu Wei Zi. (as in Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang from Jin Gui Yao Lue [Essential Prescriptions of the Golden Coffer])
iv. from Wind-Cold, Asarum with Ginger (Gan Jiang), Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi), Ephedra Ma Huang, Paeonia Bai Shao, Pinellia Ban Xia, Honey-fried Licorice (Zhi Gan Cao), Schisandra Wu Wei Zi. (as in Xiao Qing Long Tang of TCM)
v. Cough, Asthma, Asarum with Elecampane, Orris, Calamus, Licorice, Aniseed (Anti-Asthmatic Elixir, below)
vi. Asarum root (2 parts), Elecampane, Calamus, Violet root, Licorice juice (10 parts each), Aniseed (5 parts), Camphor (0.3 parts), Diluted Spirit (300 parts). (Anti-asthmatic Elixir of Boerhaave)
5. Headache, Migraine:
i. and Migraine, Asarum with Vervain and Betony
ii. from Trauma or Wind-Cold, Asarum with Bupleurum Chai Hu. (TCM)
iii. from Wind-Heat, Asarum with Rehmannia Sheng Di Huang (TCM)
iv. from exterior Wind-Cold, Asarum with Ephedra Ma Huang, Aconitum Fu Zi, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong (as in Xi Xin San from [Pu Ji Fang (Prescriptions of Universal Relief]).
v. Migraine, Asarum with Realgar (Xiong Huang) (as in Zhi Ling San from Sheng Ji Zong Lu [Complete Record of Holy Benevolence]).
6. Headache, Toothache or bleeding painful gums and mouth sores from Stomach Heat, Asarum with Gypsum (TCM)
7. Deafness, prepared Pills from Asarum Xi Xin and Bees Wax (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
8. Chest Pain:
i. Asarum with Cinnamon and Saffron
ii. Asarum with Cinnamon twig Gui Zhi (TCM)
iii. Oils of Asarum, Galangal, Sandalwood, Long Pepper and Borneol are combined into an aerosol for acute chest pain (called Kuan Xiong aerosol or CardioVent)
9. Painful Breast Lumps, or other pain from Blood stagnation, Asarum with Angelica Dang Gui and Safflower. (TCM)
10. Fibroid Tumors, Asarum decocted in equal parts water and wine. (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
11. Edema:
i. Asarum infused in Wine and taken morning and night (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
ii. Asarum decocted in equal parts water and wine. (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
12. To Promote Menstruation:
i. Asarum with Myrrh, Cinnamon
ii. Asarum with with Myrrh, Cinnamon, Savin, Celery seed, Parsley seed, Indian Spikenard
13. As an emetic to clear Cold Phlegm:
i. Asarum with Radish seed, boiled in Hydromel or Water and Honey (Pemell, 1652)
ii. Asarum with Broom flower, Broom seed (equal parts, half dram dose), taken with Barley water. (Pemell, 1652)
iii. Asarum 18–20 grains taken with Diaturbith (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
14. Mouth and Tongue Sores and Blisters, Asarum Xi Xin and Copstis Huang Lian mixed with vinegar (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
15. Mouth Ulcers, prepare a mouthwash of Asarum Xi Xin, Artemisia capillaris, Chrysanthemum (Ju Hua), Honeysuckle, Angelica dahurica
Major Formulas:
Powder of Gum Lacca Greater (Dialacca Majores) (Mesue)
Troches of Rhubarb (Mesue)
Troches of Wormwood Greater
Hiera Picra
Antidote for Edema (Nicholas)
Antidotum Haemagogum (Nicholas)
Electuary for the Joints (Unani)
Electuary of Saffron Greater (Diacrocon Majores) (Mesue)
Electuary of Costus (Mesue)
Arabian Pills (Nicholas)
From TCM:
Du Huo Ji Sheng Tang
Ling Gan Wu Wei Jiang Xin Tang
Ma Huang Fu Zi Xi Xin Tang
She Gan Ma Huang Tang
Xiao Qing Long Tang
Zai Zao San
1. Compound (Sternatory) Powder of Asarum:
i. Asarum leaf (1 oz.), Lavenders (1 dram) (Dublin)
ii. Asarum leaf (3 parts), Marjoram, Lavender (1 part each) (Edinborough)
iii. Asarum leaf (24 parts), White Hellebore root (1 part)
iv. Asarum leaf, White Hellebore root (equal parts)
v. Asarum leaf (half oz.), Betony, Marjoram, Lily of the Valley flowers (1 oz. each) (Pharmacopoeia Generalis, 1783)
vi. Asarum leaf, Marjoram (2 drams ea.), Orris, Lavender (1 dram ea.), Clove oil (7 drops)
vii. Asarum leaf, Marjoram, Betony, Pennyroyal, Basil, Mastic, Lavender, Rosemary
2. Anti-Asthmatic Elixir:
i. Asarum root (3 parts), Florentine Orris (5 parts), Elecampane, Calamus (10 parts each), Licorice (15 parts), Aniseed (5 parts), Proof Spirit (80 parts). Infuse cold for several days, strain, and add Camphor (1 part). Dissolve. Stimulant, principally for humid Asthma.
Dose: 10–30 dops. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
Cautions:
1. Toxic in overdose. Avoid long-term use. It is a member of the Aristolchia family; some species contain high levels of safrole.
2. Not used during Pregnancy, in the very young or old. Avoid use in those with Liver or Kidney disease. Pemell (1652) said it was not for weak and tender people.
3. Not used in Yin deficiency (dryness)
4. In TCM, Asarum is considered antagonistic to Cornus Shan Zhu Yu and Astragalus. It is incompatible with Veratrum nirgum and counters the effect of Talcum.
Toxicity:
The herb is toxic and is banned in many countries due to its Safrole and Aristolchic acid content
–Long-term oral administration of Asarum heterotropoides f. mandshuricum (Maxim.) Kitag. decoction and its aristolochic acid analogs do not cause renal toxicity in mice.
–Evaluating the toxicity of the roots of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum extracted using the decoction method: Genotoxicity, single-dose toxicity, and 13-week repeated-dose toxicity studies.
Main Preparations used:
Galen:
“Its useful part is the root, and its strength is like that of sweet flag (Acorus), even stronger”.
Dioscorides:
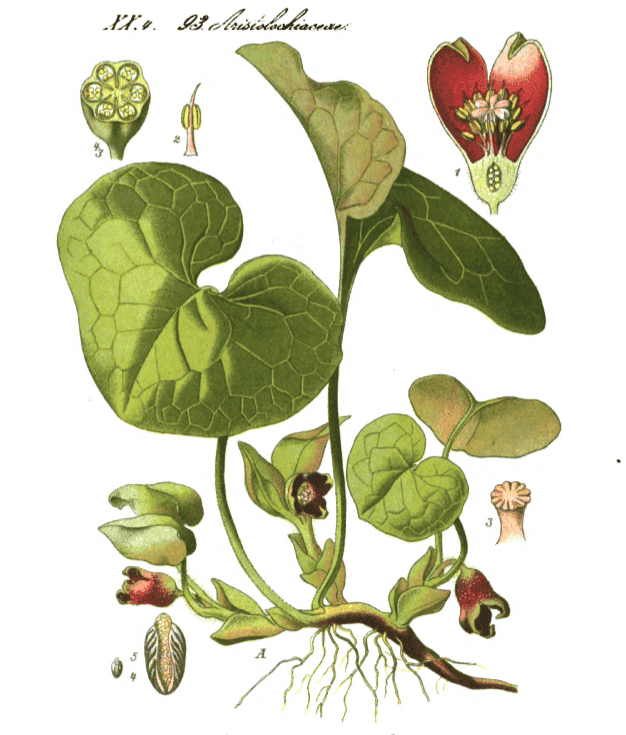
“It is called wild-nard; its leaves resemble ivy-leaves, but are smaller and more round. Its flowers, situated between the leaves near the root, are purple-coloured and resemble the flowers of the henbane (Hyoscyamus ). Its seeds are like those of the cartham. It has many roots bearing thin knots and curved like the roots of dog’s grass, but much thinner; they are fragrant, heat and prick the tongue. It grows on richly wooded mountains”.
“Al-Ghafiqi states that the original asarabacca is from Greece, although he quotes ibn Samajiin as saying that the best types are the Chinese and Spanish” (The medical formulary, or Aqrabadhīn, Al-Kindi, 1966).
This clearly shows the Chinese Asarum was known and used i the West, and that it was considered equivalent.
An Experimental History of the Materia Materia, Lewis, 1784″
The roots and leaves of asarum have a moderately strong, not very unpleasant smell, somewhat resembling that of valerian or nard ; and a nauseous bitterish, acrid taste. The roots given in substance, in doses of a scruple or more, prove strongly emetic and cathartic. The leaves have the same operation, but their dose or degree of force has not been precisely determined : according to some, they are of more activity than the roots.
It is said, that this emetic plant has been of service in serous disorders, and hurtful in melancholic cases: that in small doses, it promotes perspiration, urine, and the uterine flux: that tinctures made in spirituous liquors possess both the emetic and cathartic virtues of the asarum : but that the extracts, obtained by inspissating these tinctures, act only, and with sufficient mildness, by vomit; requiring to be given in as large doses as the plant in substance, to produce as plentiful evacuations: that infusions in water operate mildly both upwards and downwards : that by coction in water, the emetic power is first destroyed, and afterwards the purgative the decoction long boiled, or an extract prepared with a large quantity of water not acting at all by stool or vomit, but proving powerfully deobstruent, diuretic, &c. It is obvious, however,, as the activity of the asarum is diminished more and more by boiling, that both the decoction and the extract must be accompanied with one capital inconvenience, precariousness in point of strength.
The principal use of asarum among us is as an errhine. The root is one of the strongest of the vegetable substances commonly employed in this intention: a grain or two, snuffed up the nose, procure a large evacuation of mucus both from the nose and mouth, without provoking sneezing like the white hellebore root, or discovering any remarkable irritation. The leaves, though supposed to be stronger than the roots as emetics and cathartics, appear to be milder as errhines. Geoffroy relates, that after snuffing a dose of this errhine, he has observed the salutary discharge to continue for three days together, and that he has known a paralysis of the mouth and tongue cured by one dose: he recommends this medicine in stubborn disorders of the head proceeding from viscid matters, in palsies, and in soporific distempers. During its operation, the patient must carefully avoid cold; which is apt to produce pustules, inflammations, and swellings of the face, and sometimes more alarming symptoms. This herb is a principal ingredient in the cephalic or sternutatory powders of the shops: some take three parts of dried asarum and one of marjoram leaves, others equal parts of the dried leaves of asarum, marjoram, and marum syriacum, and dried lavender flowers. The empyrical herb snuffs have likewise the leaves of asarum for their basis, but often mixed with ingredients of a more dangerous nature.
GENERAL / OVERVIEW
–The genus Asarum: A review on phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology, toxicology and pharmacokinetics.
–Ethno-pharmacology of Asaroon (Asarum europaeum L.) with special reference to Unani System of Medicine.
–[Constituents of Asarum europeum L. Communication No. 18. Dynamics of the synthesis of flavonoids].
–[ANALYSIS OF THE COMPONENTS OF ASARUM EUROPEUM L. VI. DETERMINATION OF THE VOLATILE OIL AND ASARONE-(1-PROPENYL-2,4,5,-TRIMETHOXY-BENZOL) CONTENT].
–Chemical Constituents from the Roots and Rhizomes of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum and the In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity.
–[Botanical origin of commercial samples of traditional Chinese drug xixin (Herba Aasari)].
–[The Active Substances of Asarum europaeum.].
TOXICITY
–Quantitative Determination and Toxicity Evaluation of Aristolochic Acid Analogues in Asarum heterotropoides F. Schmidt (Xixin) and Traditional Chinese Patent Medicines.
–8 years post-marketing surveillance between Asari Radix and hepatocellular carcinoma: Nationwide population-based evidence against an association.
–Study on the in vivo toxic mechanism of xixin based on trace elements determination by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry.
–[Influence of single leaf Asarum himalaicum on renal function of rabbits].
–Systematic Overview of Aristolochic Acids: Nephrotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Underlying Mechanisms.
–Vitamin C attenuates the toxic effect of aristolochic acid on renal tubular cells via decreasing oxidative stress‑mediated cell death pathways.
–Reduction of safrole and methyleugenol in Asari radix et rhizoma by decoction.
ANTI-BACTERIAL
–Phenanthrene Derivatives from Asarum heterotropoides Showed Excellent Antibacterial Activity against Phytopathogenic Bacteria.
ANTI-VIRAL
–[Study on anti-HPV activity of Asarum heterotropoides].
–[Protective effect of Asarum polysaccharide on H1N1 influenza virus infection and expression of inflammatory factors].
ANTI-ALLERGIC
–Anti-allergic effects of Asarum heterotropoides on an ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis murine model.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY
–Chemical Constituents from the Roots and Rhizomes of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum and the In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity.
–[Assessment on anti-nociception and anti-inflammation pharmacodynamics of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum and Asarum sieboldii].
–[Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects in mice of water and ethanol extracts of roots and rhizomes of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum].
–[The anti-inflammatory effect of “XI XIN” [Asarum heterotropoides F. Schm. var. mandshuricum (Maxim!) Kitag.] oil (author’s transl)].
ANTI-ASTHMATIC
–Exploring the Potential Effects and Mechanisms of Asarum sieboldii Radix Essential Oil for Treatment of Asthma.
ARTHRITIS
–Salvia miltiorrhiza-asarum ointment combined with Chinese medical massage alleviates symptoms of osteoarthritis in a rat model through the Notch1/ matrix metalloproteinase-13 signaling pathway.
–Protective effect of Asarum extract in rats with adjuvant arthritis.
STROKE
–Effects of β-Asarone on Ischemic Stroke in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rats by an Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE) Pathway-Dependent Mechanism.
ANTI-DEPRESSANT
–Effect of the fragrance inhalation of essential oil from Asarum heterotropoides on depression-like behaviors in mice.
CANCER
–Asaroidoxazines from the Roots of Asarum asaroides Induce Apoptosis in Human Neuroblastoma Cells.
–(-)-Asarinin from the Roots of Asarum sieboldii Induces Apoptotic Cell Death via Caspase Activation in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells.
–Cytotoxic activity of some Asarum plants.


The Shui minority of China uses Asarum as one of the three most commonly used medicines in their system.