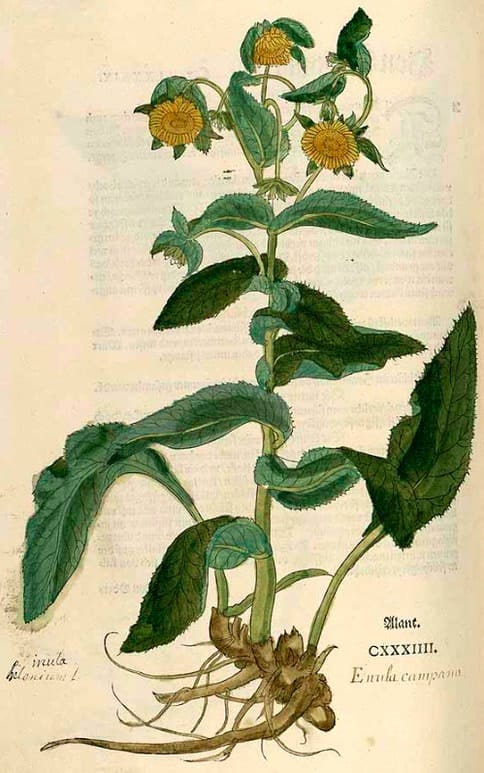
Inula, Elecampane
Also called Enulae Campane, Helenii
Inula racemosa
Rasan (Unani)
Pushkar (Ayurveda)
Ma Nu མ་ནུ (Tibetan)
Tu Mu Xiang (TCM)

Botanical name:
Inula spp.
Two main species are used:
1. I. helenium (Europe)
2. I. racemosa is used very similarly in Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, a little Bitter and Pungent
opens, cleanses, discusses
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2M. DRAWING. 2Q. ANODYNE. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3L. ANTI-TUSSIVE. 3M. ARTHRITICS
4b. OPTHALMICS. 4c. CARDIAC. 4d. PECTORAL. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4j. NERVINES. 4k. ARTHRITIC
Uses:
1. Benefits the Stomach and Spleen, clears Damp, Tonifies Qi:
-strengthens Stomach and digestion; Spleen Qi deficiency (like Atractylodes Bai Zhu)
-vomiting, diarrhea (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-Hernia, Colic, Wind, Stitches
2. Move Qi, Eases Pain:
-‘useful in all types of Cold pains’. (Avicenna)
-distention in the chest, epigastrium and hypochondria (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-bruise or sudden sprain of the Chest with pain during Breathing (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
3. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough, Strengthens the Lungs:
-all diseases of the Lungs, Cough, Asthma, shortness of Breath, Whooping Cough
-Lung Ulcers, spitting of Blood
-‘strengthening for the Heart’. (Avicenna)
4. Resists Poison, Promotes Sweat:
-biting of Rabid Dogs and other venomous Bites;
-infectious and epidemic diseases, both to prevent and cure
-Herpes, Eczema, putrid Sores and Leprosy
5. Benefits the Kidneys, Clears Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Edema, water retention, stoppage of Urine
-Gravel, Stones
-Sciatica, lower body joint pain
6. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-suppressed Menstruation, delayed or scanty Menstruation
-Pain of the Uterus
-Threatened Abortion (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
7. Clears Wind, Stops Spasms, Benefits Sinews:
-Cramps, Convulsions, Paralysis
-useful in Sciatica and Arthralgia’. (Avicenna)
-Gout, Arthritic and Rheumatic pain, Neuralgia
8. Benefits Eyesight:
-eye weakness, poor eyesight and to strengthen the sight (Decoction in Wine, Salmon)
9. Externally:
-externally for Scabs, Itch, Herpes
-old Ulcers and Sores
-fastens the Teeth if the root is chewed.
-wine decoction is gargled for toothache, loose teeth and to prevent putrefaction of the gums
-topically to the joints to tighten loose ligaments, strengthen the joints, and to help remove their pain.
-applied to Sciatica and Hemicrania
-Saline tincture (tincture in salt water) is used as a wash for Dandruff, Spots, Freckles, Herpes, Eczema etc.
Dose:
Decoction: 3–15 grams
Powder: 1500mg–5 grams
Preparation:
Correctives:
Substitutes:

Main Combinations:
1. Asthma:
i. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
ii. Tincture Against Asthma, Elecampane with … available in PRO version
iii. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
iv. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
2. Bronchitis, Elecampane with … available in PRO version
3. Whooping Cough, combine Elecampane with Thyme
4. Lung deficiency, Cough, Asthma:
i. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
5. Persistent Cough, Elecampane with … available in PRO version
6. Pectoral Elixir, Elecampane with … available in PRO version
7. Hernia, Elecampane with Rue (School of Salerno)
8. Spleen Yang and Qi deficiency, Elecampane with … available in PRO version
9. Kidney Yang Deficiency, back pain, impotence, Leukorrhea etc:
i. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
10. Promote Menstruation:
i. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
11. Paralysis:
i. Elecampane with … available in PRO version
12. Herpes, Elecampane as an ointment with … available in PRO version
Major Formulas
Decoction of Elecampane and Rue
Decoction of Horehound
Decoction to Strengthen the Lungs
Syrup for Asthma (Wirtzung)
Powder of Cinnamon Compound (Mesue)
Electuary of Clove and Costus (Caryocostinum)
Electuary for Paralysis (Wirtzung)
Electuary which is Remarkably Effective
Antidote for Cold Kidneys and to Excite Libido (Nicholas)
Tincture Against Asthma
Cautions:
1. Used cautiously during Pregnancy.
Main Preparations used:
Candied and Conserved root, Distilled Water, Extract of the Root and a Wine
‘The plant was known to the ancient writers on agriculture and natural history, and even the Roman poets were acquainted with it, and mention Inula as affording a root used both as a medicine and a condiment. Vegetius Renatus, about the beginning of the 5th century, calls it Inula Campana, and St. Isidore in the beginning of the 7th names it as Inula, adding—”quam Alum rustici vocant.” It is frequently mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon writings on medicine current in England prior to the Norman Conquest; it is also the “marchalan” of the Welsh Physicians of the 13th century and was generally well known during the middle ages. Not only was its root much employed as a medicine, but it was also candied and eaten as a sweetmeat’. (Pharmacographia, Fluckiger & Hanbury, 1879)
GENERAL / REVIEW:
–Synthetic and Pharmacological Activities of Alantolactone and Its Derivatives.
–Isoalantolactone: a review on its pharmacological effects.
–Biological Activities and Chemical Profile of Gentiana asclepiadea and Inula helenium Ethanolic Extracts.
–Bioactive sesquiterpenes from Inula helenium.
ANTIBACTERIAL:
–From Monographs to Chromatograms: The Antimicrobial Potential of Inula helenium L. (Elecampane) Naturalised in Ireland.
–Antimicrobial activity of Inula helenium L. essential oil against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Candida spp.
–In vitro activity of Inula helenium against clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains including MRSA.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY:
–Inula helenium and Grindelia squarrosa as a source of compounds with anti-inflammatory activity in human neutrophils and cultured human respiratory epithelium.
–Anti-inflammatory effects of isoalantolactone on LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia cells through activating GSK-3β-Nrf2 signaling pathway.
CONTAINS B12:
–Isolation and analysis of vitamin B12 from plant samples.
LUNG INJURY:
–Isoalantolactone suppresses LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting TRAF6 ubiquitination and alleviates acute lung injury.
–Isoalantolactone protects LPS-induced acute lung injury through Nrf2 activation.
COUGH:
–Efficacy and safety of the syrup “KalobaTUSS®” as a treatment for cough in children: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
PNEUMONIA:
–Isoalantolactone protects against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia.
TUBERCULOSIS:
–A review of medicinal plant of Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region as source in tuberculosis drug discovery.
NEUROPROTECTIVE:
–Activation of Nrf2 by costunolide provides neuroprotective effect in PC12 cells.
DEPRESSION:
–Isoalantolactone relieves depression-like behaviors in mice after chronic social defeat stress via the gut-brain axis.
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE:
–Alantolactone mitigates the elevation of blood pressure in mice induced by angiotensin II by inhibiting calcium channel activation.
DERMATITIS:
–Igalan from Inula helenium (L.) suppresses the atopic dermatitis-like response in stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes via JAK/STAT3 signaling.
–Total sesquiterpene lactones isolated from Inula helenium L. attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice.
PSORIASIS
–Alantolactone Suppresses Proliferation and the Inflammatory Response in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes and Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Skin Lesions in a Psoriasis-Like Mouse Model.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS:
–Total sesquiterpene lactones prepared from Inula helenium L. has potentials in prevention and therapy of rheumatoid arthritis.
PREBIOTIC:
–Determination of prebiotic activity and probiotic encapsulation ability of inulin type fructans obtained from Inula helenium roots.
PROTECTS FROM SMOKING DAMAGE:
–Alantolactone suppresses inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress in cigarette smoke-induced human bronchial epithelial cells through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibition of the NF-κB pathways.
ANTI-ANGIOGENIC:
–Alantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, inhibits breast cancer growth by antiangiogenic activity via blocking VEGFR2 signaling.
CYTOTOXIC:
–Cytotoxicity of some Russian ethnomedicinal plants and plant compounds.
ANTIPROLIFERATIVE:
–Antiproliferative sesquiterpene lactones from the roots of Inula helenium
ANTI-TUMOR:
–Antitumour activities of sesquiterpene lactones from Inula helenium and Inula japonica.
–[Antitumor activity of the plant remedy peptide extract PE-PM in a new mouse T-lymphoma/eukemia model].
–Tumor cell specific toxicity of Inula helenium extracts.
CANCER
–Investigation of the sensitivity of human A549 cells to paclitaxel and sesquiterpene lactone alantolactone via apoptosis induction.
–Alantolactone: A Natural Plant Extract as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Cancer.
–Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer with alantolactone and isoalantolactone.
–Tumor cell specific toxicity of Inula helenium extracts.
BREAST:
–Sesquiterpene lactones-enriched fraction of Inula helenium L. induces apoptosis through inhibition of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
–Apoptosis induction by alantolactone in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrion-dependent pathway.
–Alantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, inhibits breast cancer growth by antiangiogenic activity via blocking VEGFR2 signaling.
–Isoalantolactone inhibits the migration and invasion of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via suppression of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.
–High throughput screening of natural products for anti-mitotic effects in MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells.
–Evaluation of antitumor activity of peptide extracts from medicinal plants on the model of transplanted breast cancer in CBRB-Rb(8.17)1Iem mice.
CERVICAL:
–Alantolactone Induced Apoptosis and DNA Damage of Cervical Cancer through ATM/CHK2 Signaling Pathway.
COLORECTAL:
–The Sesquiterpene Lactone-Rich Fraction of Inula helenium L. Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Colorectal Cancer: Integrative Phytochemical, Transcriptomic, and Experimental Analyses.
–Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-dependent upregulation of death receptor 5 in human esophageal cancer cells.
ESOPHAGEAL:
–Alantolactone inhibits oesophageal adenocarcinoma cells through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-mediated reactive oxygen species increment.
–Inhibition of Growth of Esophageal Cancer by Alantolactone via Wnt/β- Catenin Signaling.
GALL BLADDER:
–Isoalantolactone suppresses gallbladder cancer progression via inhibiting the ERK signalling pathway.
GASTRIC:
–Potent inhibition of gastric cancer cells by a natural compound via inhibiting TrxR1 activity and activating ROS-mediated p38 MAPK pathway.
GLIOBLASTOMA:
–Antioxidant and anticancer activities of extract of Inula helenium (L.) in human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell line.
LEUKEMIA:
–Targeting non-oncogene ROS pathway by alantolactone in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.
–Costunolide enhances sensitivity of K562/ADR chronic myeloid leukemia cells to doxorubicin through PI3K/Akt pathway.
–Sesquiterpenoids from the roots of Inula helenium inhibit acute myelogenous leukemia progenitor cells.
–Costunolide promotes imatinib-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells via the Bcr/Abl-Stat5 pathway.
–[Antitumor activity of the plant remedy peptide extract PE-PM in a new mouse T-lymphoma/eukemia model].
LYMPHOMA:
–[Antitumor activity of the plant remedy peptide extract PE-PM in a new mouse T-lymphoma/eukemia model].
LIVER:
–Induction of Apoptosis by Isoalantolactone in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hep3B Cells through Activation of the ROS-Dependent JNK Signaling Pathway
LUNG:
–Alantolactone facilitates ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer through promoting FTH1 ubiquitination and degradation.
–Antitumor activity of alantolactone in lung cancer cell lines NCI-H1299 and Anip973.
–Alantolactone induces apoptosis, promotes STAT3 glutathionylation and enhances chemosensitivity of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells to doxorubicin via oxidative stress.
MELANOMA:
–Isocostunolide, a sesquiterpene lactone, induces mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspase-dependent apoptosis in human melanoma cells.
OSTEOSARCOMA:
–Alantolactone inhibits proliferation, metastasis and promotes apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin and MAPKs signaling pathways.
OVARIAN:
–Isoalantolactone Suppresses Glycolysis and Resensitizes Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells.
PANCREATIC:
–Isoalantolactone inhibits pancreatic cancer proliferation by regulation of PI3K and Wnt signal pathway.
–Active ingredients of Inula helenium L. exhibits similar anti-cancer effects as isoalantolactone in pancreatic cancer cells.
–Alantolactone induces apoptosis and improves chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells by impairment of autophagy-lysosome pathway via targeting TFEB.
–Ethyl acetate extract from Inula helenium L. inhibits the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating the STAT3/AKT pathway.
PROSTATE:
–Isoalantolactone Increases the Sensitivity of Prostate Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Treatment by Inducing Oxidative Stress.
TESTICULAR:
–Anticancer potential of isoalantolactone in testicular cancer: an analysis of cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and signaling pathways.
THYROID:
–Alantolactone induces concurrent apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer through ROS mitochondria-dependent caspase pathway.
SYNERGISTIC WITH CHEMOTHERAPY:
–Isoalantolactone Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin by Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species and DNA Damage.
–Alantolactone enhances gemcitabine sensitivity of lung cancer cells through the reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and Akt/GSK3β pathway.
–Costunolide enhances sensitivity of K562/ADR chronic myeloid leukemia cells to doxorubicin through PI3K/Akt pathway





1. I. helenium and I. racemosa are similar in taste, appearance and effect. Inula helenium and I. racemosa are used as the source for a type of Costus (Mu Xiang) under the name Tu Mu Xiang, indicating they are used synonymously.
2. Inula and Costus are similar and mutually benefiting, often being used together in the Eastern systems. Inula is a better Qi tonic, Costus is better to regulate Qi. In this way Inula is similar to Atractylodes Bai Zhu, another close relative with similar properties. Together, they mutually enhance. It is also noted that in some parts of China,
3. The preserved Root is a greater tonic, increases Qi and benefits Digestion. It is better for deficiency and chronic diseases of the Lungs and Kidneys; Consumption, lower body weakness, Night Sweats etc.