Scolopendrum, Hart’s Tongue
Scolopendrium, Hart’s Tongue
Deers Tongue, Horse Tongue, Lingua cervina, Hemionitis, Phyllitis

Herbarius latinus, Petri, 1485
Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563

Kurtzes Handtbuchlein, Ryff, 1599
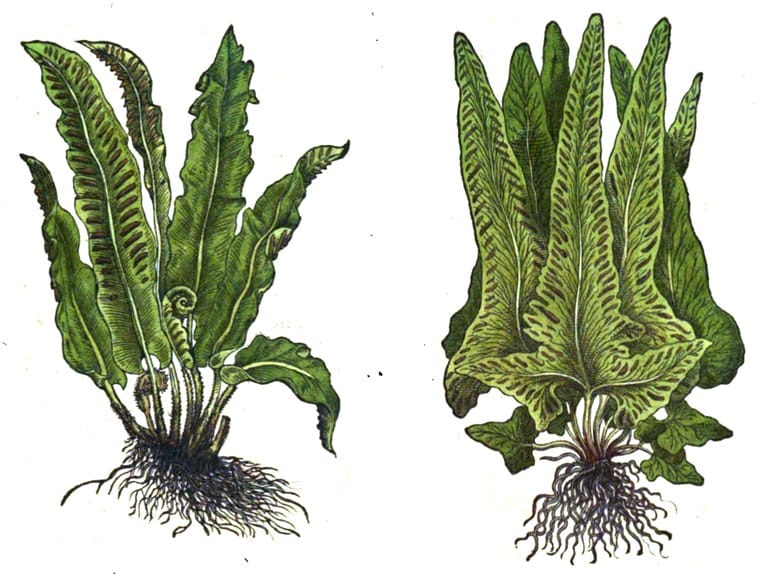
Two varieties of Scolopendrum
Left: Phyllitis; Right: Hemionitis
Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586
Scolopendrium vulgare
Medical Botany, Woodville, Hooker, 1832

Alternate varieties of Hart’s Tongue
Left: Finger Hart’s Tongue; Right: Bastard Hart’s Tongue
(Salmon, Botanologia, 1710)

Asplenium scolopendrium
(Photo by Agnieszka Kwiecień, Nova) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Scolopendrium vulgare (syn. S. officinalis, Asplenium scolopendrium)
Salmon listed several kinds of Hart Tongue:
- Common Hart’s Tongue
- Jagged Hart’s Tongue or Finger Hart’s Tongue
- Branched Hart’s Tongue
- Bastard Hart’s Tongue, which itself has three varieties:
- i. Common, True or Greater Bastard Hart’s Tongue
- ii. Lesser or Barren Hart’s Tongue
- iii. Strange Bastard Hart’s Tongue
Parts used:
Leaf
All the above-mentioned varieties share common effects.
“It is of a mild nature, and of a moderate temperament, Hot in the first degree, and dry in the second”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral, dry. Sweet
Some viewed it as mildly Warm, some as Cool.
Classifications:
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Damp, Opens Obstructions, Clears Melancholy:
-good for the Liver and Spleen
-pain, swellin, obstruction or hardness of the Spleen or Liver
-clears Damp of the Stomach, Spleen or Liver (water decoction)
-Strangury or dripping Urine
-“It is of great benefit to the Spleen when taken in drink or applied externally”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-Gravel and Stones; “If one drinks this herb, it breaks up Kidney and Bladder Stones”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-“Its leaves, decocted in vinegar, soften the spleen, and dry up its humor, when the decoction is taken for thirty days”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
2. Stops Leakages:
-Diarrhea and Dysentery (since Galen)
-Spitting of Blood
-Diabetes
3. Clears Heat, Moves the Blood:
-Palpitations, Pericarditis
-Cachexia, Chlorosis
-with alcohol (decocted in wine or tincture) for Blood stagnation and Bruising
-“strengthens the Heart”, decocted in Wine. (Dorsetn, 1540)
4. Resists Poison:
-decocted in wine for Snake bite (Dioscorides)
-acid (vinegar) tincture is also used
5. Benefits the Qi:
-“one of the six mainstays for maintaining Health” (Wittich, Vademecum, New Arzneybuch, 1594)
-“Wonderfully strengthens the Viscera” … “strengthens the Stomach and restores the Tone of the Bowels, being depraved or hurt”. (Salmon, Botanologia, 1710)
-“Strengthens the Viscera” (Medical Botany, Woodville, Hooker, 1832)
-“Scolopendra is a remedy for all diseases”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-Rickets in children
6. Externally:
-externally to cleanse Wounds and Ulcers, Burns and Scalds
-bleeding gums (decoction as a gargle)
-distilled water fastens loose gums
-applied to Hernia
-“Decocted in vinegar and applied to the spleen, it soothes swelling and pain in the spleen”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
-“chopped and boiled in wine, removes tumors/swelling (tumorem) of the spleen, applied as a plaster”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
Dose:
1. Acid (vinegar) tincture is better to open obstructions
2. Decocted in Wine is better to move the Blood and open obstructions
Decoction (water or wine): 4–6 oz.
Tincture (1 in 10): 3–9 mls. (1–3 drams)
Acid (Vinegar) tincture: add enough to a vehicle to make it pleasantly acidic.
Substitutes:
1. Ceterach and Scolopendrum were used fairly interchangeably.
2. Its use and function are similar to the other Capillary herbs, so it may be replaced with Maidenhair
Main Combinations:
One of the Five Capillary herbs
1. Cleanse the Blood, Skin diseases, Leprosy Hart’s Tongue with Fumitory, Endive, Wormwood, Dodder, Hops (as in Syrup of Fumitory Compound)
2. Scrofula: “The leaves are crushed; mixed with Hyssop, boiled in wine; drunk, cure scrofula and stranguria”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
3. Pericarditis, Hart’s Tongue, Calendula, Tansy, Vervain, Valerian
4. Heat of the Stomach or Liver, Hart’s Tongue with Golden Seal
5. Spleen pain: “If one drinks wisely from wine in which Scolopendria and Tamarisk have been boiled, it undoubtedly removes pain in the spleen”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
6. Strangury: “The leaves are crushed; mixed with Hyssop, boiled in wine; drunk, cure scrofula and stranguria”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
7. Dripping Urine: “Wine made with Scolopendria and Parsley root, this drink is beneficial for the dripping urine”. (Dorsetn, 1540)
8. Diabetes, Hart’s Tongue with Golden Seal
9. Hernia, Hart’s Tongue, Knotgrass, Comfrey root (equal parts) decoct in water and drink internally while applying the cooked herbs externally. (Culpeper)
Major Formulas:
Syrup of Fumitory Compound (Augustana)
Syrup of Senna Comp
Syrup to Purge all Humors of Frankfurt
Electuary of Currants, Electuarium de Corruns
Electuary of Saffron Greater (Diacrocon Majores) (Mesue)
1. Bitter Powder:
Wormwood 3 handfuls
Blessed Thistle
Hart’s Tongue
Lesser Centaury 1 handful each
Elecampane ½ oz.
Orris 1 oz.
Calamus ½ oz.
Orange peel 6 drams
Powder. (Palatine)
2. Febrifuge Decoction (Apozem)
Root of Patience 1 dram
Elecampane 2 drams
Chicory leaf
Burnet leaf 1 handful each
Hart’s Tongue leaf 3
Live Crabs bruised 2
Wood Lice bruised 10–12
Camomile
Peach flowers 1 or 2 pugils
Cinchona
Rhubarb
Cascarilla 1 dram each
Water 1 pound
Boil for an hour. To be taken in 2 doses, the first with 2 oz. of Syrup of Peach flowers, the second with 1 oz. of Compound Syrup of Smallage. (Pierquin)
3. Bitter Essence:
Tansy 1 oz.
Hart’s Tongue
Blessed Thistle
Lesser Centaury
Gentian
Herb Patience 3 drams each
Fresh unripe
Orange peel ½ oz.
Alcohol 12 oz.
Digest, express, filter.
Tonic, stomachic, carminative, anthelmintic.
Dose: 50–70 drops in wine. (Wirtemburg)
Cautions:
Very dry. Not suitable for Yin deficiency.

